Formatting CoreMS data for ftmsRanalysis
Natalie Winans
2025-05-23
Source:vignettes/read_CoreMS_data.Rmd
read_CoreMS_data.RmdThe ftmsRanalysis package allows users to read in data
from CSV files containing high resolution mass spectrometry data after
initial processing and formula assignment.
Reading in data from CSV files
The function read_CoreMS_data takes one or more CSV
files output by the software CoreMS and converts them into a single
data.frame that is compatible with
ftmsRanalysis functions. The function will automatically
insert a column containing the file names and output a
data.frame that has been assigned the class
CoreMSrbind. Files are read in by providing a list of file
paths, either manually or by pattern matching using a function like
list.files, as in the example below.
library(ftmsRanalysis)
library(dplyr)
ex_files <- list.files(pattern = "ex_data")
dat <- read_CoreMS_data(ex_files)At this point, it is good practice to check the dataset to verify whether there are isotopic columns present, and if so, which ones. This information will be used in the next step.
Converting to CoreMSData Object
The next step is to convert the CoreMSrbind object into
a CoreMSData object using the function
as.CoreMSData. The arguments for this function are the
data.frame output by the function
read_CoreMS_data and, optionally, the names of the columns
corresponding to mass-to-error ratio (m/z), peak height, mass error,
confidence score, molecular formula, and other peak metadata. The
default values for these parameters are set to the column names in
typical CoreMS output. The column names corresponding to isotope columns
C13, S34, O18, and N15 should be included if and only if present in the
dataset. In this case, we will include names for the C13 and O18
columns.
cmsDat <- as.CoreMSData(dat)The CoreMSData object consists of a list of two
data.frames, monoiso_data and
iso_data, containing the monoisotopic peaks and isotopic
peaks, respectively. At this time, the isotopic peaks are not used for
downstream analyses.
Plotting CoreMSData Object
Calling the plot method on a CoreMSData object produces a barplot
showing the number of peaks, both monoisotopic and isotopic, with unique
masses per file/sample. In a case with many samples or very long sample
names, the parameter rotate_x_labs can be set to
TRUE. This will display the x-axis tick labels vertically
for improved readability.
plot(cmsDat)Filtering by Confidence Score
Confidence filtering is performed using the functions
conf_filter and apply.Filt. We first construct
a confFilter object using the function
conf_filter. Before applying a filter, the
confFilter object can be plotted to visualize the numbers
of monoisotopic peaks retained in the dataset under different confidence
filtering thresholds.
cmsDat_filt_obj <- conf_filter(cmsDat)
plot(cmsDat_filt_obj)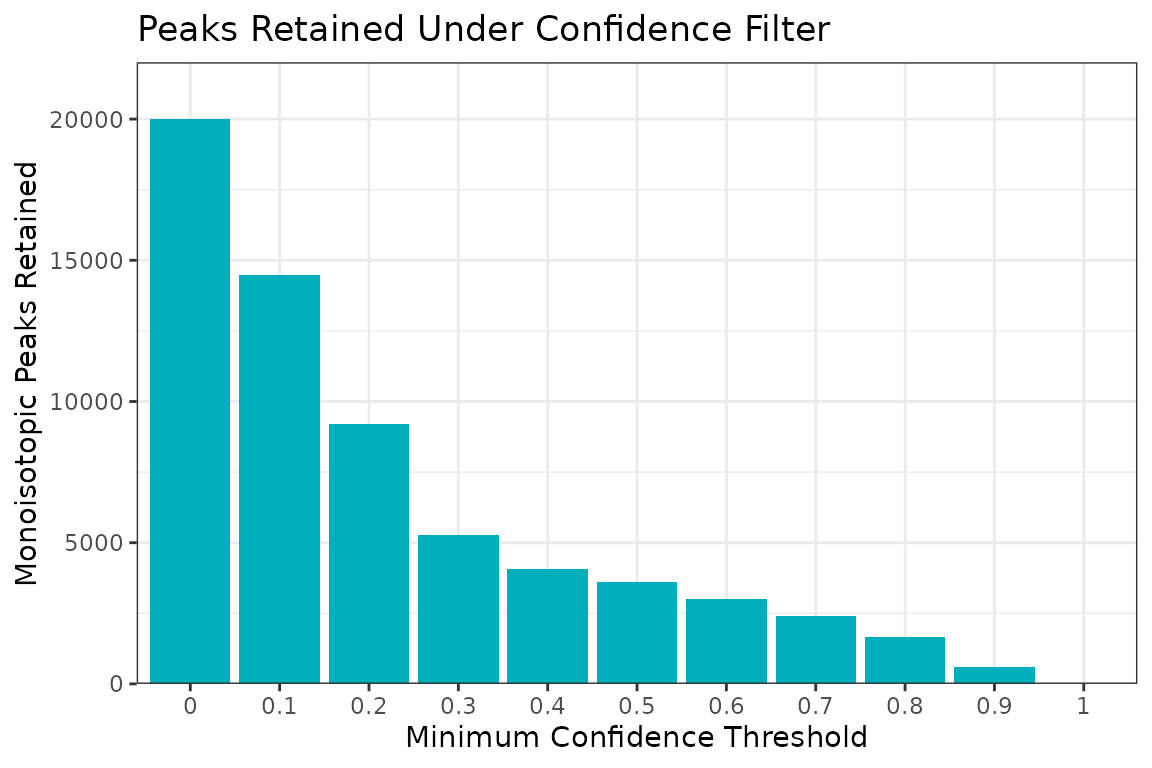
The mass_error_plot function provides a quick summary of
the dataset as well as another method for previewing the impact of a
confidence filter on the dataset before application, using the optional
parameter, min_conf. These plots show only monoisotopic
peaks.
plotly::subplot(mass_error_plot(cmsDat),
mass_error_plot(cmsDat, min_conf = 0.25),
mass_error_plot(cmsDat, min_conf = 0.50),
mass_error_plot(cmsDat, min_conf = 0.75),
nrows = 2, shareX = TRUE,
titleX = TRUE, titleY = TRUE,
margin = 0.05)When plotting a dataset with 1000 or more peaks, the
mass_error_plot function will return a hex plot in which
the color indicates the number of points in a region, while a dataset
with fewer than 1000 peaks will return a scatter plot with information
about individual peaks available by hovering over points.
mass_error_plot(cmsDat, min_conf = 0.95)Once an appropriate confidence threshold has been selected, apply the
confidence filter using the function applyFilt, specifying
the confFilt object, the CoreMSData object,
and the desired minimum confidence threshold, min_conf.
cmsDat_filtered <- applyFilt(filter_object = cmsDat_filt_obj,
msObj = cmsDat,
min_conf = 0.5)The filtered dataset object contains attributes indicating that a
filter has been applied, including the confidence threshold and a list
of the mass identifiers of the removed peaks. These values can be
accessed using the attr function.
attr(cmsDat_filtered, "filters")$confFilt$report_text## [1] "A confidence filter was applied to the data, removing peaks with a confidence score of less than 0.5. A total of 19157 monoisotopic peaks were removed by this filter including 2436 missing values. A total of 5235 isotopic peaks were removed by this filter including 0 missing values."If an attempt is made to apply a confidence filter to a dataset that has already been filtered by confidence score, an error will be thrown to indicate this.
applyFilt(filter_object = cmsDat_filt_obj,
msObj = cmsDat_filtered,
min_conf = 0.8)## Error in applyFilt.confFilt(filter_object = cmsDat_filt_obj, msObj = cmsDat_filtered, : A confidence filter has already been applied to this dataset using a 'min_conf' of 0.5Assigning Unique Molecular Formulas to Peaks
ftmsRanalysis functions require that each sample in a
dataset contains only unique m/z values and unique molecular formulas.
Since CoreMS outputs several candidate formula assignments
for each peak, we must apply the function
unique_mf_assignment to reduce the dataset to unique
values. This step can be performed using one of three criteria: maximum
confidence score (method = "confidence"), maximum peak
height (method = peak_intensity"), or prevalence across
samples (method = "prevalence").
If this function is called on a dataset that has not been adequately confidence filtered, it is likely that ties will be present in the dataset. In this case, an error message will provide a minimum confidence score threshold that must be applied to the dataset before assigning unique molecular formulas.
cmsDat_unique_mf <- unique_mf_assignment(cmsDat, method = "confidence")## Error in unique_mf_assignment(cmsDat, method = "confidence"): Data set contains tied confidence scores. Apply a confidence filter at a threshold of at least 0.16.
cmsDat_unique_mf <- cmsDat %>%
applyFilt(filter_object = cmsDat_filt_obj,
msObj = .,
min_conf = 0.16) %>%
unique_mf_assignment(method = "confidence")Convert CoreMSData object into ftmsData object
Once unique molecular formulas have been assigned to peaks within
each sample, we can convert the CoreMSData object into an
ftmsData object using the function
coreMSDataToFtmsData. This transforms the data table
containing monoisotopic peaks into a list of three data tables:
-
e_data: Expression data- Rows correspond to unique peaks observed, with Mass column containing unique m/z values
- Remaining columns correspond to samples, values are peak intensities
-
f_data: Sample data- Rows correspond to samples, additional columns may be added containing sample metadata
-
e_meta: Molecular identification data- Rows correspond to unique peaks observed
- Elemental columns contain counts/molecular formulae
- Additional columns contain other CoreMS-output peak metadata
ftmsObj <- coreMSDataToFtmsData(cmsDat_unique_mf)For further steps and information, see this introduction to
ftmsRanalysis.x